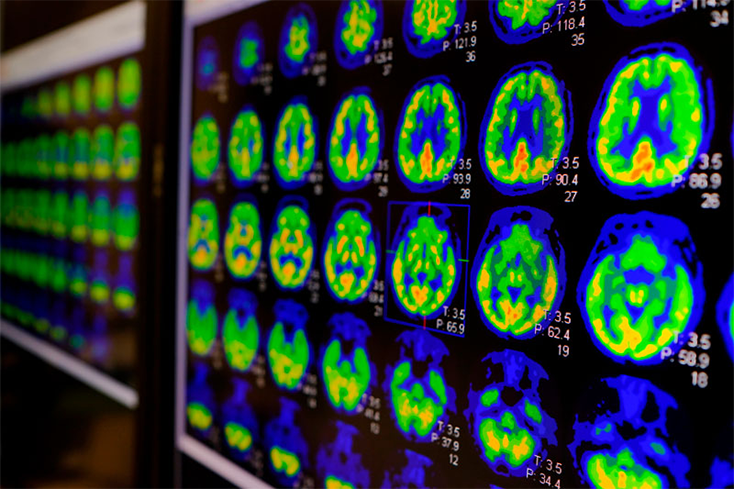
In studies carried out in different cohorts, the TP42/40 ratio has made it possible to discriminate patients with cortical beta-amyloid (Aβ) pathology confirmed by positron emission tomography (Aβ-PET positive) from those who are Aβ-PET negative with sensitivities between 77-89% and negative predictive value (NPV) between 64-97% which are highly relevant values for a screening test.
Examples:
Plasma TP42/40 ratio levels correlated significantly with Aβ-PET levels measured in in Standardized Uptake Value Ratio (SUVR) and Aβ42.
Additionally, the lower the TP42/40 ratio, the faster the Aβ-PET-SUVR increases and the higher the risk of developing dementia in patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).